
EMS Muscle Stimulator Machine: Does EMS Benefit Inflammation?
2025-11-24 15:30
Many people use EMS muscle stimulator machines to enhance muscle strength, improve blood circulation, or accelerate recovery. However, whether EMS (Electrical Muscle Stimulation) is beneficial for inflammation remains a question.
This article will systematically analyze the principles and mechanisms of electric muscle stimulator machines and their potential impact on inflammation, and answer related questions.
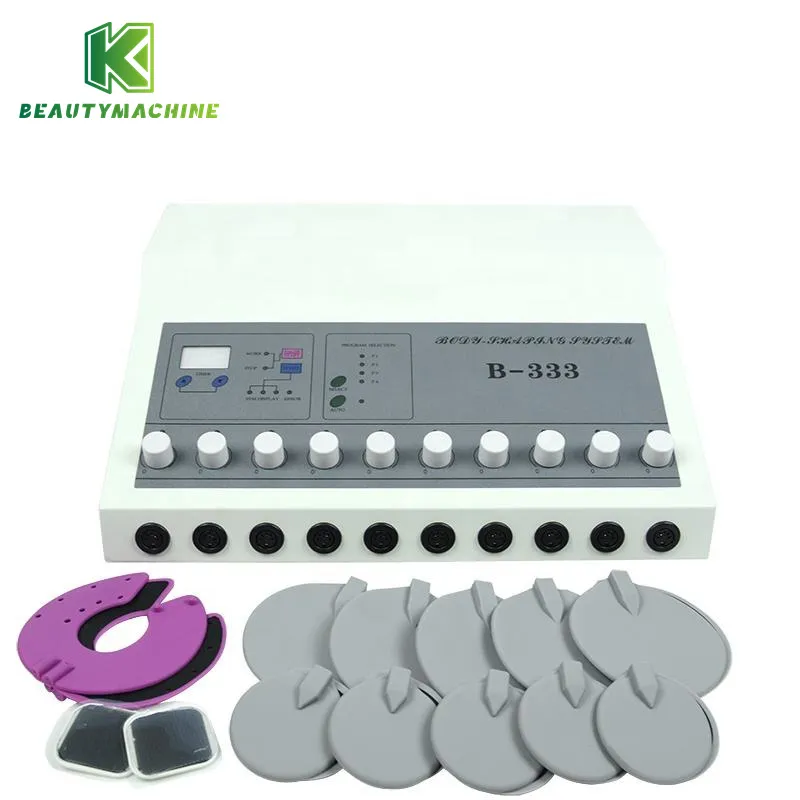

What is an EMS muscle stimulator machine?
An EMS muscle stimulator machine is a device that delivers low-frequency electrical pulses to muscles through skin electrodes, inducing muscle contraction. It was initially used in medical rehabilitation, such as muscle recovery after sports injuries and prevention of muscle atrophy. In recent years, the application of EMS has expanded to fitness, body shaping, and home physiotherapy, becoming a non-invasive method of muscle training.
The working principle of EMS mainly includes the following aspects:
• Electrical pulse stimulation: Electrical stimulation is transmitted to nerve endings through surface electrodes, mimicking the motor nerve signals sent by the brain, causing the muscles to contract actively.
• Muscle Fiber Activation: The electric muscle stimulator machine can activate deep muscle fibers, including those that are difficult to fully utilize during normal exercise, thus improving muscle strength.
• Improved Local Blood Circulation: Muscle contraction promotes local blood flow, increasing oxygen and nutrient supply, which aids in tissue repair.
It can be seen that the EMS muscle stimulator machine not only trains muscles but may also have a certain impact on inflammation by improving blood circulation and neural responses.
What is the basic mechanism of action of EMS on inflammation?
Inflammation is an immune response, typically involving local vasodilation, leukocyte infiltration, release of inflammatory factors, and tissue repair. During this process, blood circulation, neural reflexes, and cellular metabolic levels all influence the development and relief of inflammation.
The main mechanisms by which EMS may act on inflammation are as follows:
1). Improved Local Blood Circulation
The muscle contraction induced by the EMS muscle stimulator machine can increase local blood flow, promoting the transport of oxygen, nutrients, and immune cells to the site of inflammation and accelerating the removal of metabolic waste. Improved blood flow helps alleviate chronic inflammation caused by tissue hypoxia.
2). Enhanced Lymphatic Flow
Muscle contraction promotes lymphatic circulation, helping to drain cellular waste and excess fluid from inflamed areas. This plays a role in reducing edema and inflammation.
3). Neuromodulation
EMS stimulation of muscles also affects the local nervous system, potentially indirectly influencing inflammation by regulating the secretion of inflammatory factors through neurotransmitters.
4). Reduction of Secondary Inflammation Due to Muscle Weakness
Prolonged inactivity or muscle atrophy can lead to chronic local inflammation. Moderate muscle stimulation using an EMS muscle stimulator machine can maintain muscle tone and reduce the risk of inflammation induced by muscle weakness.
In summary, the EMS muscle stimulator machine theoretically has a certain auxiliary effect in alleviating inflammation, but its effectiveness is closely related to the stimulation intensity, frequency, treatment site, and type of inflammation.
How do EMS affect acute and chronic inflammation differently?
Inflammation can be divided into acute and chronic inflammation, and the mechanisms of action of the EMS muscle stimulator machine differ between the two.
1. Acute Inflammation
Acute inflammation typically manifests as redness, swelling, heat, and pain, representing the body's immediate response to injury or infection. Caution should be exercised when using an EMS muscle stimulator machine in this situation, as overstimulation may increase local blood flow and tissue load, thus worsening pain or swelling. Therefore, during the acute inflammatory phase, low-intensity EMS should be used moderately to avoid exacerbating the inflammation.
2. Chronic Inflammation
Chronic inflammation is common due to prolonged muscle inactivity, joint degenerative changes, or chronic pain. EMS can alleviate tissue discomfort caused by chronic inflammation by improving muscle activity, blood circulation, and lymphatic flow. Long-term, regular use of an electric muscle stimulator machine can help maintain muscle health, thereby indirectly reducing inflammation levels.
How to Safely Use an EMS Muscle Stimulator Machine to Assist in Inflammation Relief?
While an EMS muscle stimulator machine may offer some relief for inflammation, improper use can also pose risks. The following are safety guidelines:
1. Control Intensity and Frequency
Excessive intensity from the electric muscle stimulator machine may cause excessive muscle contraction, which could actually worsen local inflammation. 1. **Choose a low to moderate intensity that suits your tolerance and follow the device instructions to set a reasonable frequency and duration.**
2. Choose the appropriate area
For inflamed areas, avoid using high-intensity EMS directly on areas of acute injury or significant swelling. Start by using it on surrounding or healthy muscles to promote overall blood circulation.
3. Coordinate with rest and rehabilitation
The electric muscle stimulator machine is an adjunct tool and cannot replace rest, rehabilitation training, or professional treatment. Schedule EMS use appropriately, avoiding prolonged stimulation of the same muscle group.
4. Consider your personal health condition
People with heart disease, pregnant women, those with broken skin, or those with implanted electronic devices should use the EMS muscle stimulator machine under the guidance of a doctor.

Can EMS replace traditional anti-inflammatory treatment?
The EMS muscle stimulator machine's effect on inflammation is primarily adjunctive, indirectly relieving inflammation by improving blood circulation, enhancing muscle activity, and lymphatic flow. However, it cannot directly replace medication, physical therapy, or rehabilitation training. Professional medical treatment is still necessary in cases of severe inflammation or during the acute phase. EMS is best suited as an adjunct tool for rehabilitation and inflammation management, rather than a monotherapy.
What is the current state of scientific research on EMS for inflammation?
Multiple experimental and clinical studies have shown that electric muscle stimulators (EMS) are effective in improving blood circulation, increasing muscle strength, and relieving chronic muscle discomfort. For example:
• EMS can increase local blood flow and promote the removal of metabolic waste products.
• In rehabilitation training for chronic muscle atrophy or degenerative joint inflammation, EMS can improve muscle tone and function.
However, research on its direct anti-inflammatory effects is still limited, and the effects depend on individual differences, the type of inflammation, and the parameters of the electric muscle stimulator. Therefore, EMS should be understood as an adjunct tool, not a panacea for inflammation.
Will EMS worsen inflammation?
In cases of acute inflammation or high-intensity stimulation, the EMS muscle stimulator may increase blood flow or muscle load, thereby worsening swelling or pain. Therefore, it should be used at low intensity or temporarily suspended during acute inflammation.
Does EMS need to be used daily?
For the adjunctive management of chronic inflammation, short-term use of the EMS muscle stimulator machine (e.g., 15–20 minutes daily) is sufficient. Overuse may not necessarily bring greater benefits and could even cause muscle fatigue.
Can EMS be used alone for inflammation management?
The EMS muscle stimulator machine should be used as an adjunct tool, in conjunction with appropriate rest, rehabilitation training, and professional treatment to effectively manage inflammation.
Does EMS benefit inflammation?
Yes, it does. The EMS muscle stimulator machine primarily improves blood and lymphatic circulation through muscle contraction, indirectly affecting inflammation. Its adjunctive effect on chronic inflammation is more significant, but caution should be exercised when using it for acute inflammation.
EMS cannot replace medication or professional treatment; it can only be used as an adjunct tool for rehabilitation and inflammation management. The key to safe use of the electric muscle stimulator machine is controlling the intensity, choosing the appropriate site, scheduling usage frequency reasonably, and considering individual health conditions.
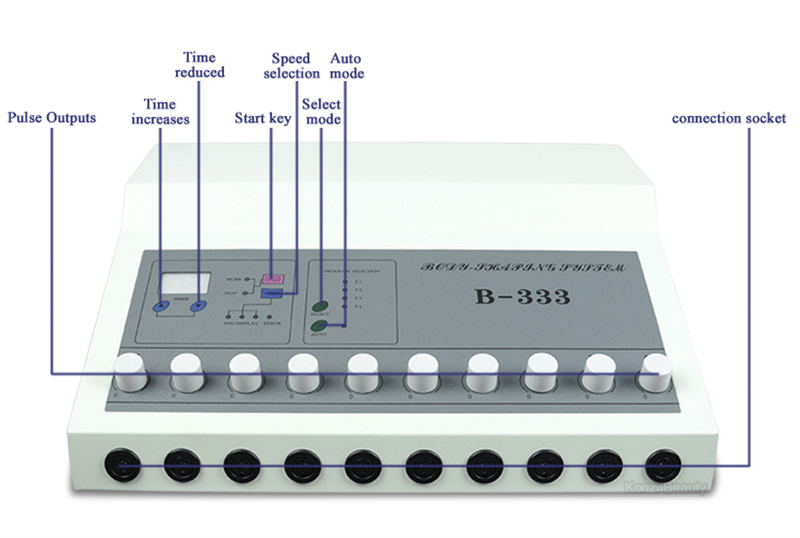
What makes KuoHai’s factory production different?
KuoHai owns a modern manufacturing facility in Foshan, China, equipped with advanced assembly lines and precision testing systems. Unlike trading companies, we control every step of production—from material sourcing to final inspection. This allows us to maintain high-quality standards while keeping factory prices low.
Customers can buy directly from the source, enjoy customized OEM service, and trust in our consistent production capacity for bulk purchasing and wholesale supply.
Get the latest price? We'll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)







